Understanding RAID configurations is crucial for your computer or network’s performance and data security when setting up storage. RAID stores data across multiple hard disks to protect against drive failures.
The most common RAID levels, RAID 0 and RAID 5 offer different advantages based on user needs, from speed and capacity to redundancy and reliability. This blog will dive into RAID 0 and RAID 5’s key features, benefits, and considerations, helping you choose the best RAID configuration for your storage requirements.
RAID 0 Basics
RAID 0 is a storage solution that merges several physical hard drives into one logical unit, enhancing the system’s overall storage capability. This is achieved by distributing data across the drives in a way that improves performance and increases storage capacity.
RAID 0 is also known as striping because it divides data into stripes and writes them across all the drives in the array.
RAID 0 is often chosen for applications that demand high performance, such as video editing or gaming, where speed is more critical than data redundancy.

However, RAID 0, lacking redundancy, isn’t suited for critical data without backup. For those looking to balance performance with data security, other RAID configurations, like RAID 1 or RAID 5, maybe more appropriate choices, offering redundancy at the expense of some performance.
RAID 5 Basics
RAID 5 is a storage technology that combines multiple hard drives into one logical unit. However, unlike RAID 0, which focuses on performance and capacity, RAID 5 prioritizes data redundancy and fault tolerance. It uses a technique known as parity to store redundant data on the drives in the array.
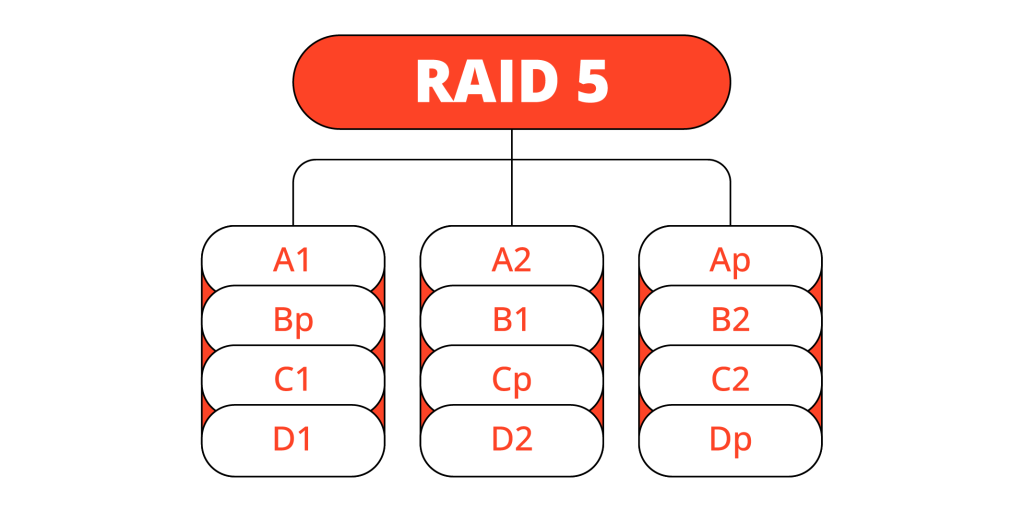
RAID 5 requires at least three physical hard drives. Data is distributed across all the drives along with parity information, which is used to reconstruct any lost data in case of a drive failure.
This allows for both improved performance and data protection. However, since parity data is also stored on the drives, RAID 5 has a slightly lower storage capacity compared to RAID 0.
Additionally, the process of rebuilding data in RAID 5 can be time-consuming, especially with larger drives. Despite this, RAID 5 remains a popular choice for systems where balancing data availability, space efficiency, and security is crucial.
Comparing RAID 0 and RAID 5
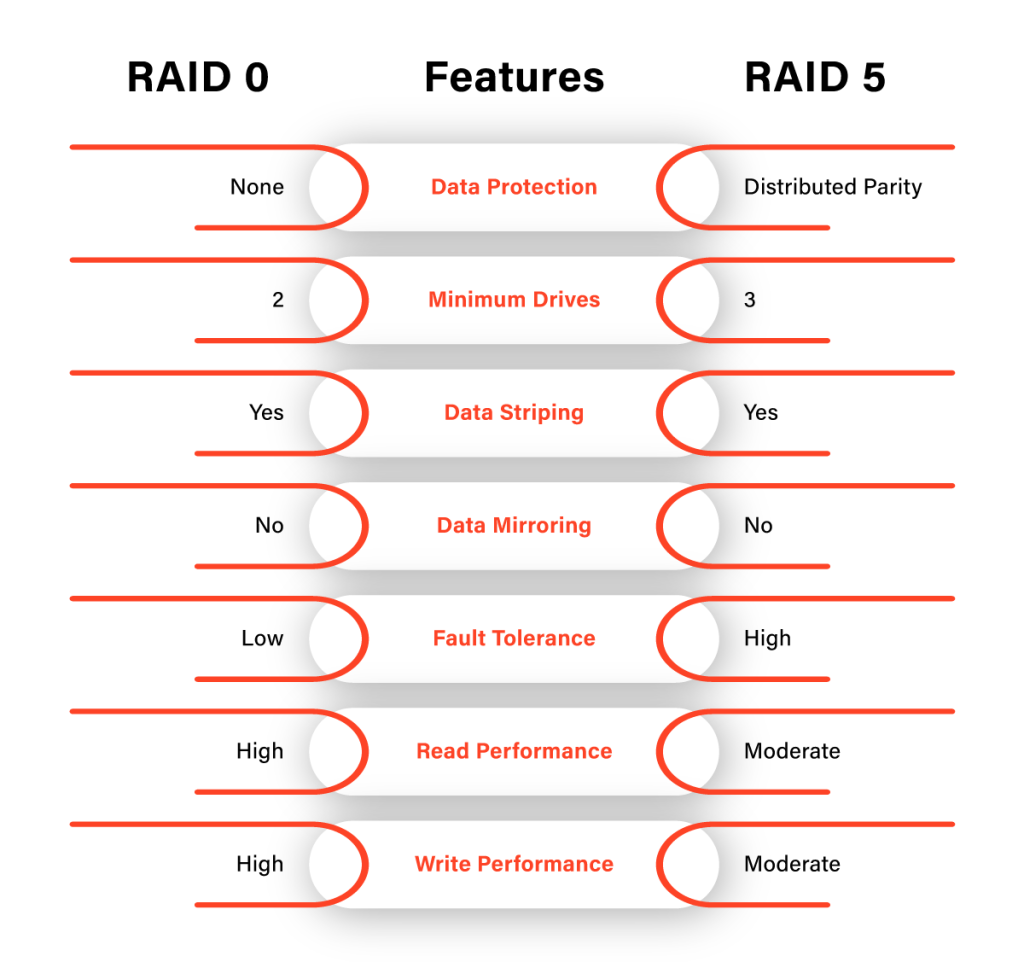
Both RAID 0 and RAID 5 have their advantages and limitations. The main difference between the two is their focus – RAID 0 prioritizes performance and capacity, while RAID 5 prioritizes data protection.
Write Performance
Due to its striping technique, RAID 0 has better write performance than RAID 5. However, since data is spread across multiple drives in RAID 0, a single drive failure can result in data loss. On the other hand, RAID 5’s parity information allows for improved write performance and data protection.
Minimum Drives
RAID 0 needs at least two drives; RAID 5 requires a minimum of three. This means that RAID 5 has slightly higher hardware costs and is more complex to set up. RAID 5 provides better data protection, tolerating a single drive failure without data loss.
Data Striping
RAID 0 stripes data across all drives, while RAID 5 stripes data along with parity information. This means that RAID 0 has better performance and capacity, but no redundancy, while RAID 5 offers both improved performance and data protection.
Data Mirroring
RAID 0 does not have any mirroring capabilities, meaning there is no duplicate data stored on the drives. On the other hand, RAID 5 has a form of data mirroring through its parity information, allowing for improved fault tolerance.
Fault Tolerance
RAID 0 has no fault tolerance, meaning all data is lost if one drive fails. On the other hand, RAID 5 can tolerate a single drive failure and still maintain data integrity through its parity information.
Read Performance
RAID 0 has the best read performance out of all RAID levels, as data is distributed across multiple drives. This allows for faster access to data compared to other RAID configurations, including RAID 5. However, RAID 5 still offers improved read speeds compared to a single drive setup.
Capacity Comparison between RAID 0 and RAID 5
RAID 0 provides the maximum storage capacity since it combines the total storage space of all drives in the array without using any of it for redundancy. This means if you have two 1TB drives in a RAID 0 setup, you get a total of 2TB usable storage.
In contrast, RAID 5 requires one drive’s capacity to store parity information, reducing the total available storage.
For instance, in a three 1TB drive RAID 5 setup, one drive’s space is used for parity, leaving the user with approximately 2TB of usable storage.
Despite this reduction in capacity, the advantage of RAID 5 lies in its ability to provide data protection through redundancy, offering a balance between storage space and data safety.

This means that even if one drive fails, the system can reconstruct the lost data using the parity information, ensuring that no data is lost. This makes RAID 5 an ideal solution for systems where data availability and security are crucial, without requiring the full duplication of data as seen in RAID 1 setups.
Which RAID configuration is best for you?
Choosing the right RAID configuration depends on your specific storage needs. If you require high performance and maximum capacity, then RAID 0 may be a suitable option. However, if data protection and fault tolerance are more critical, then RAID 5 would be a better choice. Ultimately, it’s essential to consider your budget, data accessibility, and required storage capacity when deciding which RAID configuration is best for you.
Additionally, some systems support both RAID 0 and RAID 5 setups, allowing you to have the benefits of both configurations by creating different arrays for different types of data. It’s crucial to know your needs and consider the pros and cons before choosing the best RAID configuration for you.
FAQ - RAID 0 vs RAID 5 Configuration
How does RAID 0 differ from RAID 5?
RAID 0 boosts performance and capacity by spreading data across multiple disks without backup, risking data loss if a drive fails. RAID 5, however, spreads data and adds parity for fault tolerance, surviving a single drive failure.
Is RAID 0 or RAID 5 better for gaming?
For gaming, RAID 0 might be more beneficial due to its superior performance and maximum storage capacity. However, RAID 5’s fault tolerance makes it a safer option for storing critical game files that you cannot afford to lose.
Can I convert from RAID 0 to RAID 5?
Converting directly from RAID 0 to RAID 5 is not straightforward and typically involves backing up data, reconfiguring the RAID setup, and restoring the data. It’s important to consult your RAID controller’s documentation for specific instructions and capabilities.
Do I need a special RAID controller to use RAID 5?
Yes, RAID 5 requires a RAID controller that supports the RAID 5 configuration. This can be a hardware controller or software-based, depending on your system setup.
Is RAID 0 suitable for data backup purposes?
RAID 0 isn’t fit for data backup since it lacks redundancy or fault tolerance. If a single drive fails in a RAID 0 setup, all data is lost. It’s crucial to regularly back up important data on a separate storage solution if using RAID 0.